GitHub and GitLab
GitHub Action
The Terrascan GitHub Action can be used as part of GitHub workflows to scan your repository for IaC issues as part of code pushes or pull requests.
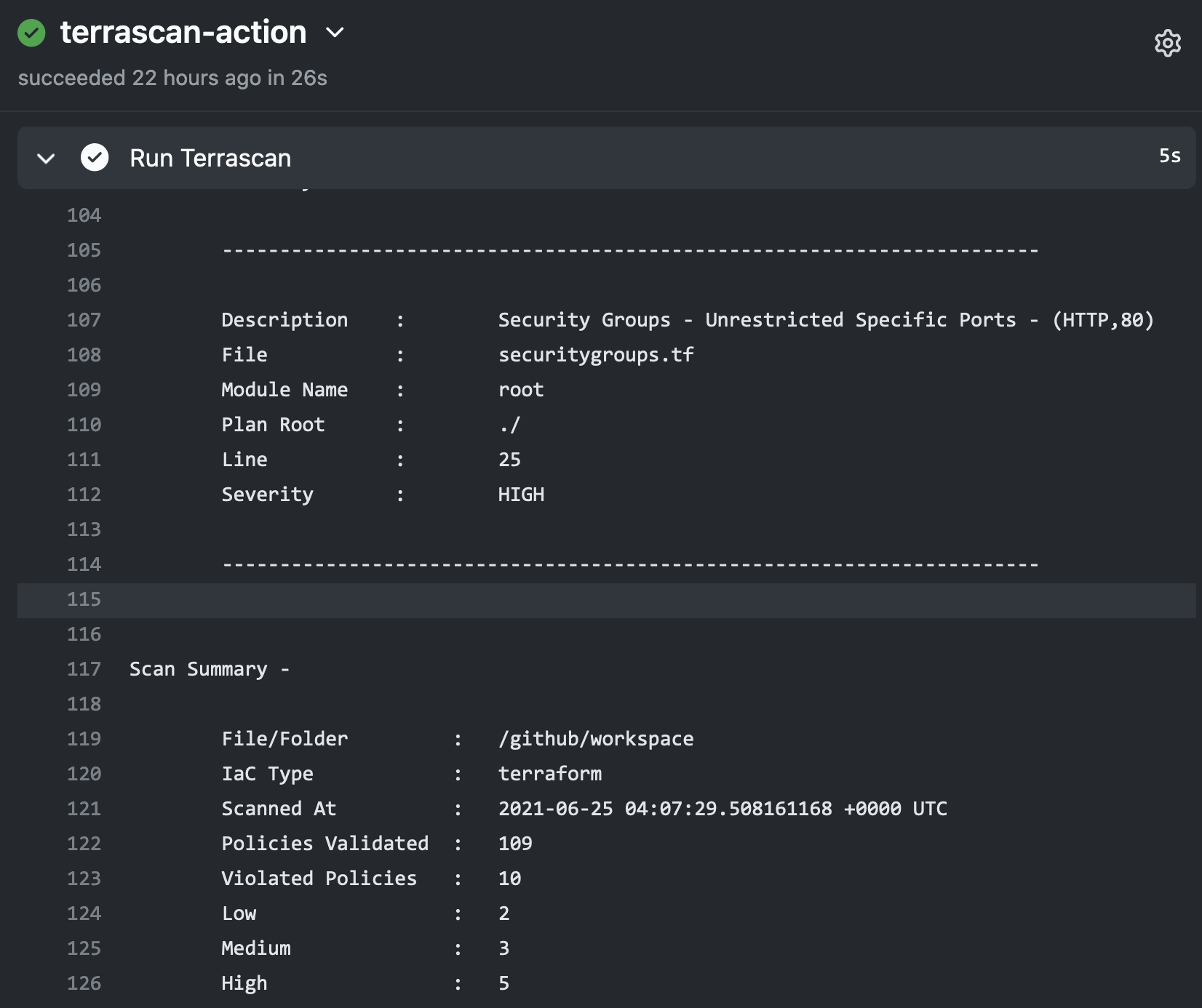
Using Terrascan’s SARIF output, the action can include issues found during the scan within GitHub’s code scanning results for the repository.
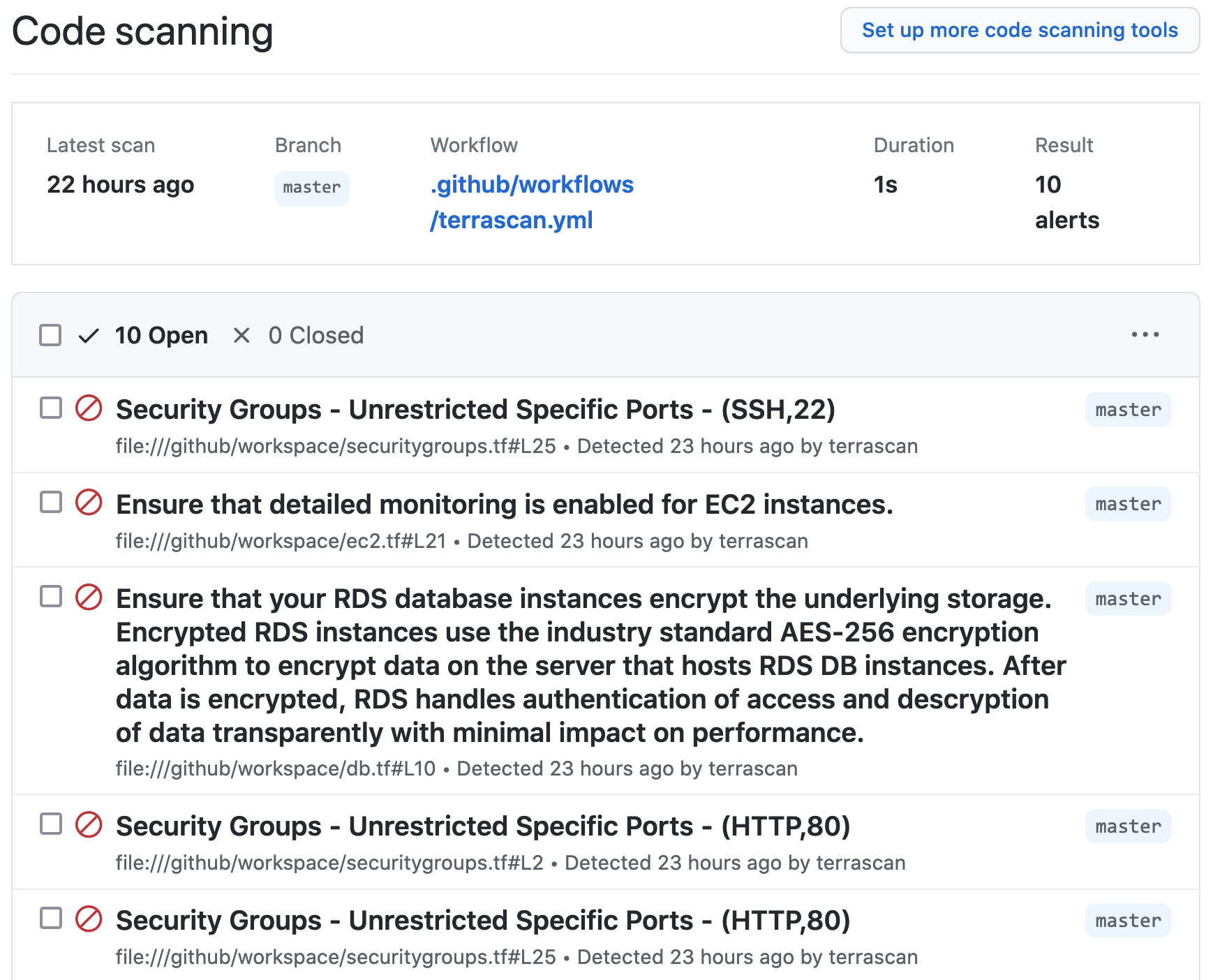
Below is an example workflow configuration where the action is configured to scan a repository including Terraform v14+ HCL files for AWS resources and the SARIF output of the scan is uploaded to GitHub code scanning.
on: [push]
jobs:
terrascan_job:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
name: terrascan-action
steps:
- name: Checkout repository
uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Run Terrascan
id: terrascan
uses: tenable/terrascan-action@main
with:
iac_type: 'terraform'
iac_version: 'v14'
policy_type: 'aws'
only_warn: true
sarif_upload: true
#non_recursive:
#iac_dir:
#policy_path:
#skip_rules:
#config_path:
- name: Upload SARIF file
uses: github/codeql-action/upload-sarif@v1
with:
sarif_file: terrascan.sarif
A detailed explanation of the action’s input variables is available in the terrascan-action repository.
GitLab CI
GitLab CI can use Docker images as part of a pipeline. We can take advantage of this functionality and use Terrascan’s docker image as part of your pipeline to scan infrastructure as code.
To do this you can update your .gitlab-ci.yml file to use the “accurics/terrascan:latest” image with the [“bin/sh”, “-c”] entrypoint. Terrascan can be found on “/go/bin” in the image and you can use any Terrascan command line options according to your needs. Here’s an example .gitlab-ci.yml file:
stages:
- scan
terrascan:
image:
name: tenable/terrascan:latest
entrypoint: ["/bin/sh", "-c"]
stage: scan
script:
- /go/bin/terrascan scan .
Argo CD Application PreSync Hooks
Terrascan can be configured as an Argo CD job during the application sync process using resource hooks. The PreSync resource hook is the best way to evaluate the kubernetes deployment configuration and report any violations.
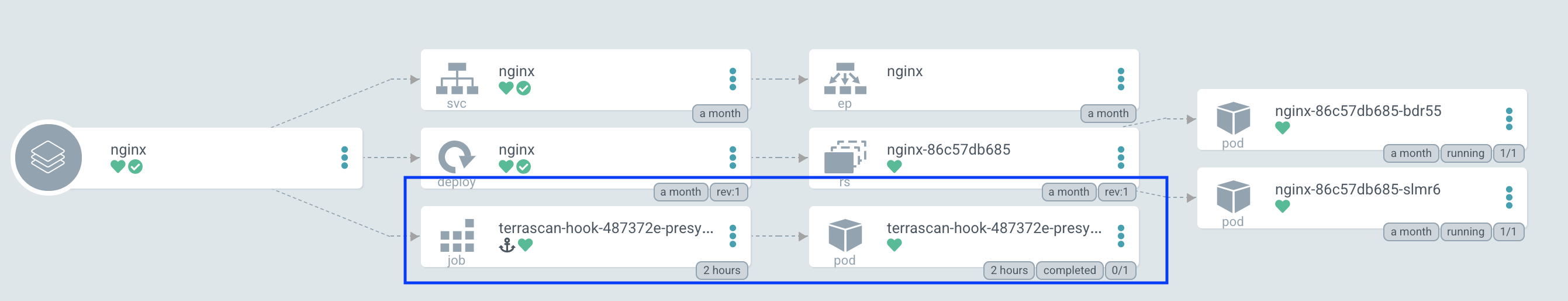
Adding the Terrascan job consists of two steps:
- Creating a container which runs Terrascan
- Configuring a PreSync hook which uses that container
We’ll address the PreSync hook first.
Step 1: Configure PreSync resource hook
The following example hooks yaml is mostly ready to be added to an existing kubernetes configuration. Just make sure the secrets volume is relevant, specify your new Terrascan container image, and make sure the embedded script scans your repo and sends notifications to your Slack webhook endpoint.
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
generateName: terrascan-hook-
annotations:
argocd.argoproj.io/hook: PreSync
spec:
ttlSecondsAfterFinished: 3600
template:
spec:
volumes:
- name: secret-volume
secret:
secretName: ssh-key-secret
containers:
- name: terrascan-argocd
image: "<your container namespace>/<your container build from step #2 below>:<hash>"
command: ["/bin/ash", "-c"]
args:
- >
cp /etc/secret-volume/ssh-privatekey /home/terrascan/.ssh/id_rsa &&
chmod 400 /home/terrascan/.ssh/id_rsa &&
/go/bin/terrascan scan -r git -u <git URL to scan> -i k8s -t k8s | /home/terrascan/bin/notify_slack.sh webhook-tests argo-cd https://hooks.slack.com/services/TXXXXXXXX/XXXXXXXXXXX/0XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
volumeMounts:
- name: secret-volume
readOnly: true
mountPath: "/etc/secret-volume"
restartPolicy: Never
backoffLimit: 1
As shown, the PreSync requires access to the repository where IaC is stored, using the same branch (default) as the Argo CD application pipeline.
For non-public repositories, the private key needs to be added as a kubernetes secret.
kubectl create secret generic ssh-key-secret \
--from-file=ssh-privatekey=/path/to/.ssh/id_rsa \
--from-file=ssh-publickey=/path/to/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
Configuring the job to delete only after the specified time see ttlSecondsAfterFinished will allow users to check for violations in the User Interface, the alternative is through notifications.
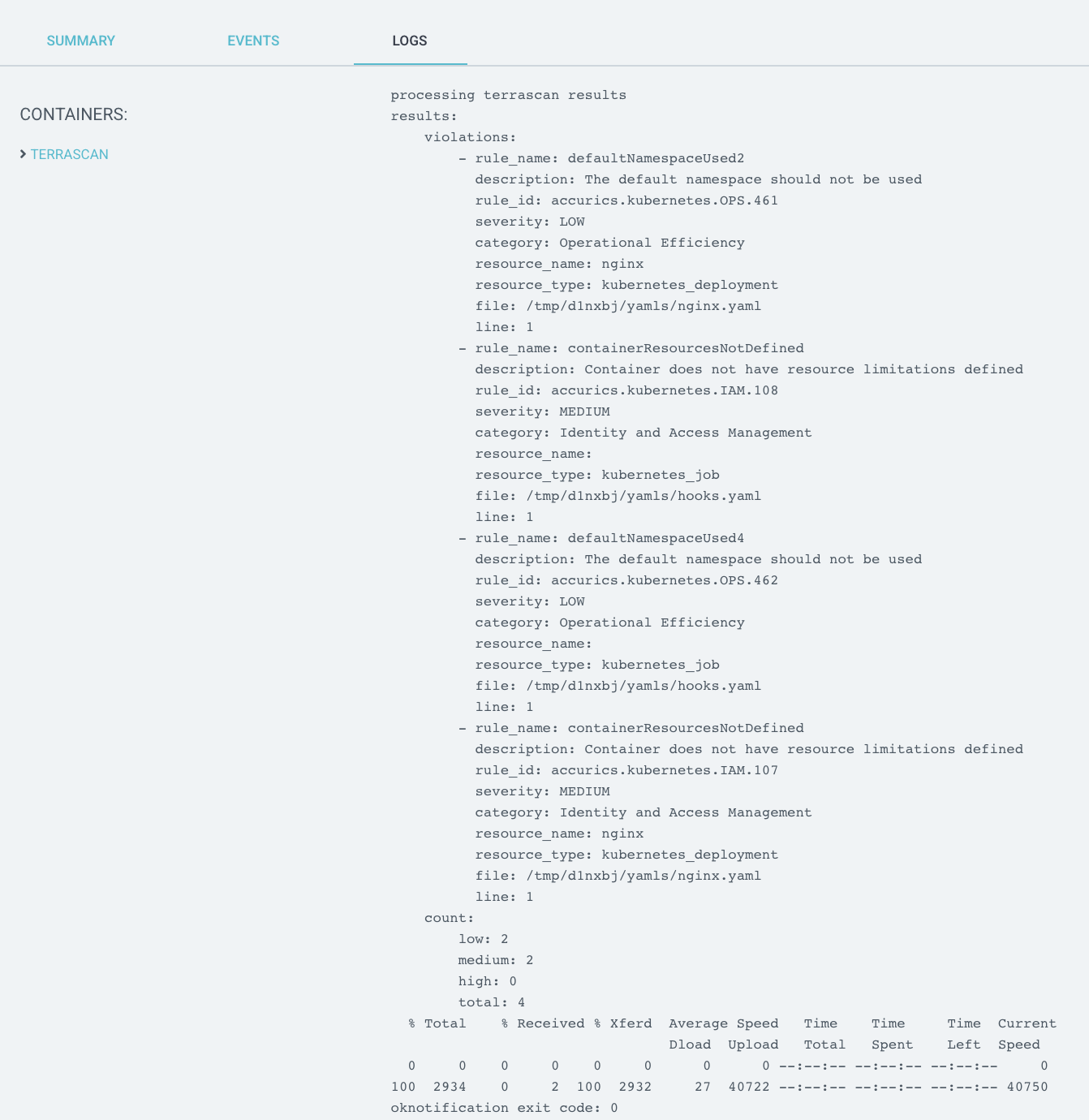
Step 2: Create Terrascan container
The container which runs Terrascan can be built using the following files: known_hosts, notify_slack.sh, Dockerfile.
known_hosts
The known_hosts file ensures that the container will be able to clone your project’s git repository in order to scan it. Hashes for the most common public repository hosts are included here, and you may add hashes for any private hosts which you need to access in order to clone your project.
# known_hosts
github.com,192.30.255.113 ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAABIwAAAQEAq2A7hRGmdnm9tUDbO9IDSwBK6TbQa+PXYPCPy6rbTrTtw7PHkccKrpp0yVhp5HdEIcKr6pLlVDBfOLX9QUsyCOV0wzfjIJNlGEYsdlLJizHhbn2mUjvSAHQqZETYP81eFzLQNnPHt4EVVUh7VfDESU84KezmD5QlWpXLmvU31/yMf+Se8xhHTvKSCZIFImWwoG6mbUoWf9nzpIoaSjB+weqqUUmpaaasXVal72J+UX2B+2RPW3RcT0eOzQgqlJL3RKrTJvdsjE3JEAvGq3lGHSZXy28G3skua2SmVi/w4yCE6gbODqnTWlg7+wC604ydGXA8VJiS5ap43JXiUFFAaQ==
bitbucket.org,104.192.141.1 ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAABIwAAAQEAubiN81eDcafrgMeLzaFPsw2kNvEcqTKl/VqLat/MaB33pZy0y3rJZtnqwR2qOOvbwKZYKiEO1O6VqNEBxKvJJelCq0dTXWT5pbO2gDXC6h6QDXCaHo6pOHGPUy+YBaGQRGuSusMEASYiWunYN0vCAI8QaXnWMXNMdFP3jHAJH0eDsoiGnLPBlBp4TNm6rYI74nMzgz3B9IikW4WVK+dc8KZJZWYjAuORU3jc1c/NPskD2ASinf8v3xnfXeukU0sJ5N6m5E8VLjObPEO+mN2t/FZTMZLiFqPWc/ALSqnMnnhwrNi2rbfg/rd/IpL8Le3pSBne8+seeFVBoGqzHM9yXw==
gitlab.com,172.65.251.78 ecdsa-sha2-nistp256 AAAAE2VjZHNhLXNoYTItbmlzdHAyNTYAAAAIbmlzdHAyNTYAAABBBFSMqzJeV9rUzU4kWitGjeR4PWSa29SPqJ1fVkhtj3Hw9xjLVXVYrU9QlYWrOLXBpQ6KWjbjTDTdDkoohFzgbEY=
notify_slack.sh
The notify_slack.sh script is used to send a Slack notification after the scan completes. This example expects the channel name, username, and webhook URL to be passed as command line arguments from the PreSync hook which invokes this container. You may modify this script if you wish to send notifications in a different way.
#!/bin/ash
# notify_slack.sh
function send_slack_notificaton {
channel=$1
username=$2
slack_hook=$3
curl -X POST --data-urlencode payload="{\"channel\": \"#${channel}\", \"username\": \"${username}\", \"text\": \" \`\`\` $(cat results.out) \`\`\` \", \"icon_emoji\": \":ghost:\"}" ${slack_hook}
}
if [ -p /dev/stdin ]; then
echo "processing terrascan results"
while IFS= read line; do
echo "${line}" | tr '\\"' ' ' >> results.out
done
cat results.out
send_slack_notificaton $1 $2 $3
echo "notification exit code: $?"
else
echo "no response skipping"
fi
Dockerfile
The Dockerfile is, of course, used to build the container. In this case, we start with the official Terrascan image and we add in the above files to ensure we can access the repository and send notifications.
# Dockerfile
FROM tenable/terrascan:929e377
ENTRYPOINT []
USER root
RUN apk add --no-cache openssh curl
WORKDIR /home/terrascan
RUN mkdir -p .ssh && mkdir -p bin
COPY known_hosts .ssh
COPY notify_slack.sh bin/
RUN chown -R terrascan:terrascan .ssh && \
chown -R terrascan:terrascan bin && \
chmod 400 .ssh/known_hosts && \
chmod u+x bin/notify_slack.sh
USER terrascan
CMD ["ash"]
Once you’ve built the image and pushed to your container registry, you can add the PreSync hook which will automatically run Terrascan during the application sync process.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.